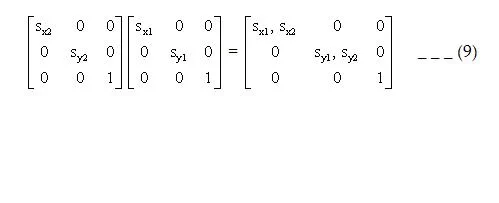Composite transformation Matrix can be obtained by calculating. The matrix product of the individual transformations forming products of transformation matrix is often referred to as concatenation or composition of matrices.
- Translation : If two successive translation vectors (tx1, ty1) and (tx2, ty2) are applied to a coordinate position P, final transformed location P’ is calculated as :
P’ = T (tx2, ty2) . {T (tx1, ty1) . P} = {T(tx2, ty2) .T(tx1, ty1)} . P _ _ _ (3)
Where P and P’ are represented as homogenous – coordinate column vectors. We can verify this result by calculating the matrix product for the tow associative groupings. Composite Matrix for this sequence is :
 Or T(tx2, ty2) . T(tx1, ty1) = T(tx1 + tx2, ty1 + ty2) _ _ _ (5)
Which shows that two successive translations are additive.
Or T(tx2, ty2) . T(tx1, ty1) = T(tx1 + tx2, ty1 + ty2) _ _ _ (5)
Which shows that two successive translations are additive. - Rotations : Two successive rotations applied to point P produce the transformed position : P’ = R(θ2). {P(θ1). P} = {R(θ2). R(θ1)}. P _ _ (6) By multiplying 2–rotation matrices, we can verify that two successive rotations are additive : R(θ2). R(θ1) = R(θ1+ θ2) _ _ _ (7) So that final rotated coordinates can be calculated with the composite rotation matrix as : P’ = R(θ1+ θ2) . P _ _ _ (8)
- Scaling: Concatenating transformation matrices for 2-successive scaling operations produce the following composite scaling matrix:
Or S(Sx1, Sy2). S(Sx1, Sy1) = S(Sx1 . Sx2 , Sy1 . Sy2) _ _ (10) The resulting matrix in this case indicates that successive scaling operations are multiplicative. That is if we were to triple the size of an object twice in successive the final size would be nine times that of the original.
Author: Anju Bhatt